Multimedia Gallery
Nanoscale drug carriers injected into subcutaneous tissue
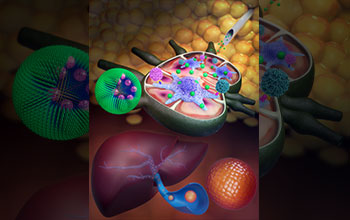
(Top): In this image, nanoscale drug carriers known as polymersomes are injected into subcutaneous tissue, allowing them to reach specific types of immune cells that reside within lymph nodes. This effectively teaches the immune system what it should and should not reject. These immune cells are known as antigen presenting cells (light purple/lavender cells with many appendages). (Bottom): As a result of this training, the immune system does not reject foreign pancreatic islet cells, which are obtained from a donor and injected into the portal vein of a recipient’s liver as a treatment for Type 1 diabetes.
[Research supported by U.S. National Science Foundation grants DGE 1842165, CBET 1453576 and DMR 0960140.]
Learn more in the Northwestern University news story Nanotherapy offers new hope for the treatment of Type 1 diabetes. (Date image taken: Dec. 2021; date originally posted to NSF Multimedia Gallery: March 1, 2022)
Credit: Prof. Evan Scott, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Northwestern University; illustration by Alex D. Jerez
Images and other media in the National Science Foundation Multimedia Gallery are available for use in print and electronic material by NSF employees, members of the media, university staff, teachers and the general public. All media in the gallery are intended for personal, educational and nonprofit/non-commercial use only.
Images credited to the National Science Foundation, a federal agency, are in the public domain. The images were created by employees of the United States Government as part of their official duties or prepared by contractors as "works for hire" for NSF. You may freely use NSF-credited images and, at your discretion, credit NSF with a "Courtesy: National Science Foundation" notation.
Additional information about general usage can be found in Conditions.
Also Available:
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (5.2 MB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.

 All images in this series
All images in this series