All Images
News Release 12-109
All the Colors of a High-Energy Rainbow, in a Tightly Focused Beam
Tabletop laser-like device can create multicolor beam of ultraviolet light, X-rays, and the wavelengths in between
This material is available primarily for archival purposes. Telephone numbers or other contact information may be out of date; please see current contact information at media contacts.

This art represents an electron being ripped from an atom by a strong laser field, which stretches its quantum wave function over hundreds of atomic sizes. Just as electrons accelerated in an X-ray tube emit bremsstrahlung radiation, electrons accelerated by a laser can emit rainbows of coherent X-rays in a laser-like beam. X-ray light is "invisible to the human eye but is important for being able to 'see' the fine details and fastest motions of the nanoworld."
Credit: Tenio Popmintchev, JILA and University of Colorado at Boulder
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (1.1 MB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.
Margaret Murnane, Henry Kapteyn and Tenio Popmintchev--all of the NSF Engineering Research Center for Extreme Ultraviolet Science and Technology--describe their new technology for creating a laser-like beam of light that incorporates light from the UV, X-rays and all the wavelengths in between.
Credit: National Science Foundation
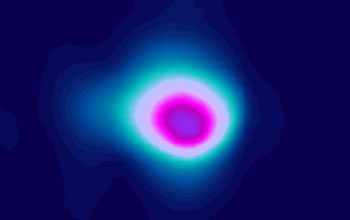
This picture shows an image of a coherent (laser-like) X-ray beam as it impacts a surface. In contrast to the incoherent (light-bulb-like) light emitted in all directions from a Roentgen X-ray tube, the X-rays produced by high harmonic generation (HHG) emerge as well-directed, laser-like, beams.
Credit: Tenio Popmintchev, JILA and University of Colorado at Boulder
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (396 KB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.

This image depicts the experimental setup used to create a coherent version of the Roentgen tube in the soft X-ray region of the spectrum. When a long-wavelength, femtosecond laser is focused into this hollow waveguide filled with high-pressure helium gas, part of the laser is converted into an ultrafast, laser-like, X-ray beam.
Credit: Tenio Popmintchev, JILA and University of Colorado at Boulder
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (5.3 MB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.
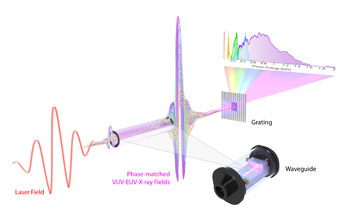
Illustration of the experimental setup used to create a coherent version of the Roentgen tube in the soft X-ray region of the spectrum. When a long-wavelength femtosecond laser is focused into a hollow waveguide filled with high-pressure helium gas, part of the laser is converted into an ultra-fast, laser-like, X-ray beam. The extreme nonlinear laser-matter interaction generates a broad range of light wavelengths, spanning the electromagnetic spectrum from the ultraviolet (UV) to the X-ray region. The generated UV-to-X-ray light is "amplified" as it propagates through the gas medium since all the electromagnetic fields add up constructively.
Credit: Tenio Popmintchev and Brad Baxley, JILA and University of Colorado at Boulder
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (936 KB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.
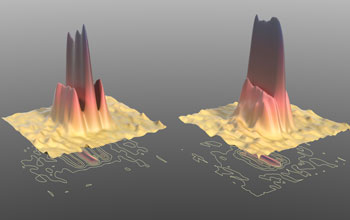
When a Young's double slit is illuminated by a coherent, laser-like, beam, light from each slit can interfere and form a diffraction pattern, due to constructive and destructive interferences between light transmitted through each slit. These interference (or diffraction) patterns show that the kiloelectron-volt (keV) high-harmonic beams are laser-like.
Credit: Tenio Popmintchev and Brad Baxley, JILA and University of Colorado at Boulder
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (1.3 MB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.

The researchers' work is described in the June 8, 2012 issue of the journal Science.
Credit: Copyright AAAS 2012
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (1.4 MB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.
